
Tax Planning For Salaried Employees
Most of the employees are worried that a part of their salary is taken away from them as tax
deductions. We cannot avoid the income tax however, there are certain deductions which
helps us to reduce the Income tax. Tax planning helps us to make a huge saving on tax
expenses. Well, here are some of sections from the Income tax act, 1961 which would be
useful for salaried employees to save taxes.
Section 80C: This section provides deduction for various investment and payments made. It
includes the following:
- Payment of annual premium of a Life insurance policy
- Tuition fee paid for education of Children
- Fixed deposit in a scheduled bank or post office for 5 years or more
- Employee’s contribution to statutory provident fund and recognized provident fund.
- Amount invested in NSC as well as interest accrued on NSC
- Repayment of loan taken for purchase or construction of house
- Deposit in notified bonds of NABARD
- Deposit in Senior citizen savings scheme
- Contribution towards Unit Linked Insurance Plan (ULIP)
- Notified units of Mutual funds or UTI
- Stamp duty and registration fee for acquisition of house property
- Deposit in sukanya samridhi scheme
Section 80CCC: Contribution to pension fund of LIC or other insurance Company
Section 80CCD(1): Contribution to pension scheme of Central Govt./Notified pension
scheme/Atal pension yojna
Section 80CCE: This section restricts the aggregate deduction u/s 80C + 80CCC + 80CCD(1) to
maximum of Rs. 1,50,000/-
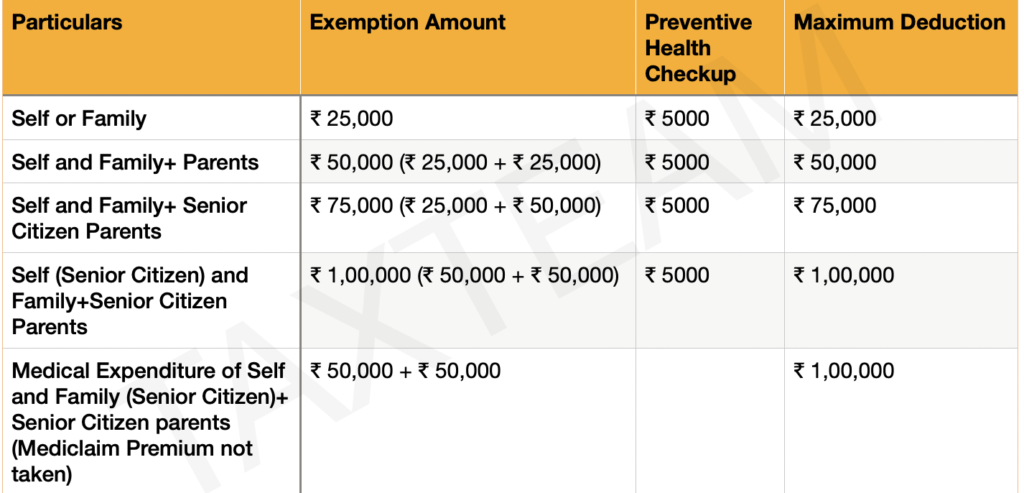
Section 80D: Deduction in respect of medical insurance premium, preventive health check-
up, and medical expenditure for senior citizen where medical insurance premium is not
available.
Section 80E: Deduction in respect of interest on loan for higher education in India or abroad
Section 80EE and Section 80EEA: Deduction in respect of interest on housing loan.
Section 80EEB: Deduction in respect of interest on electric vehicle loan
Section 80TTA: Deduction of Interest on savings account upto Rs. 10,000/-
These are some of the common deductions available to reduce tax for individual tax payers. Salaried employees can make use of these options and do their tax planning accordingly.


